Bootstrap Modal Form
Introduction
In some instances we truly need to set the focus on a targeted details remaining anything others faded behind making confident we have actually gained the visitor's consideration or perhaps have plenties of data needed to be easily accessible from the page yet so vast it surely might bore and dismiss the person digging the web page.
For these types of events the modal component is absolutely valuable. Precisely what it works on is showing a dialog box taking a vast field of the screen diming out whatever else.
The Bootstrap 4 framework has everything desired for generating such component with the minimum initiatives and a easy intuitive structure.
Bootstrap Modal Event is structured, still, variable dialog assists powered by JavaScript. They assist a lot of help cases from user notification ending with fully customized web content and include a number of useful subcomponents, sizings, and a lot more.
How Bootstrap Modal Position performs
Right before starting with Bootstrap's modal component, ensure to check out the following as Bootstrap menu options have recently replaced.
- Modals are designed with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They are really positioned over everything else in the documentation and remove scroll from the <body> to make sure that modal content scrolls instead.
- Clicking on the modal "backdrop" will automatically close the modal.
- Bootstrap only supports a single modal pane simultaneously. Nested modals usually aren't supported while we consider them to remain poor user experiences.
- Modals use position:fixed, which have the ability to in some cases be a bit particular about its rendering. Whenever it is possible, put your modal HTML in a high-level location to prevent potential disturbance directly from some other components. When nesting a.modal within another fixed element, you'll likely run into issues.
- One once more , due to position: fixed, certainly there are a few cautions with applying modals on mobile tools.
- In conclusion, the autofocus HTML attribute has absolutely no affect in modals. Here is actually the way you can possibly reach the exact same result by having custom made JavaScript.
Keep reading for demos and usage suggestions.
- As a result of how HTML5 defines its semantics, the autofocus HTML attribute comes with no result in Bootstrap modals. To reach the same effect, use some custom made JavaScript:
$('#myModal').on('shown.bs.modal', function ()
$('#myInput').focus()
)To set up we need a trigger-- an anchor or tab to get clicked on in order the modal to become displayed. To achieve so simply specify data-toggle=" modal" attribute followed via specifying the modal ID like
data-target="#myModal-ID"
Example
And now why don't we generate the Bootstrap Modal Validation in itself-- first we require a wrapper component including the entire thing-- delegate it .modal class to it.
A smart idea would definitely be at the same time adding in the .fade class for receive great developing transition upon the showcase of the element.
If those two don't match the trigger won't actually fire the modal up, you would also want to add the same ID which you have defined in the modal trigger since otherwise.
The moment that has been executed we require an added element possessing the actual modal web content-- assign the .modal-dialog class to it and eventually-- the .modal-sm on the other hand
.modal-lg to include various modifications to the proportions the element will get on display. Once the sizing has been built it's time to handle the web content-- develop one more wrapper by having the .modal-content within and fill it having some wrappers such as .modal-header for the top part and .modal-body for the certain material the modal will carry within.
Additionally you might possibly desire to put in a close button within the header delegating it the class .close as well as data-dismiss="modal" attribute yet it is not a condition due to the fact that in case the user clicks on away in the greyed out part of the display the modal gets dismissed in any case.
Essentially this id the design the modal features have within the Bootstrap framework and it pretty much has stayed the same in both Bootstrap version 3 and 4. The brand-new version includes a bunch of new solutions although it seems that the developers team assumed the modals do work all right the way they are so they directed their care out of them so far.
Now, lets us check out at the several sorts of modals and their code.
Modal components
Shown below is a static modal sample ( suggesting the position and display have been overridden). Included are the modal header, modal body (required for padding), and modal footer ( optionally available). We ask that you incorporate modal headers with dismiss actions any time you can, or perhaps provide some other precise dismiss action.
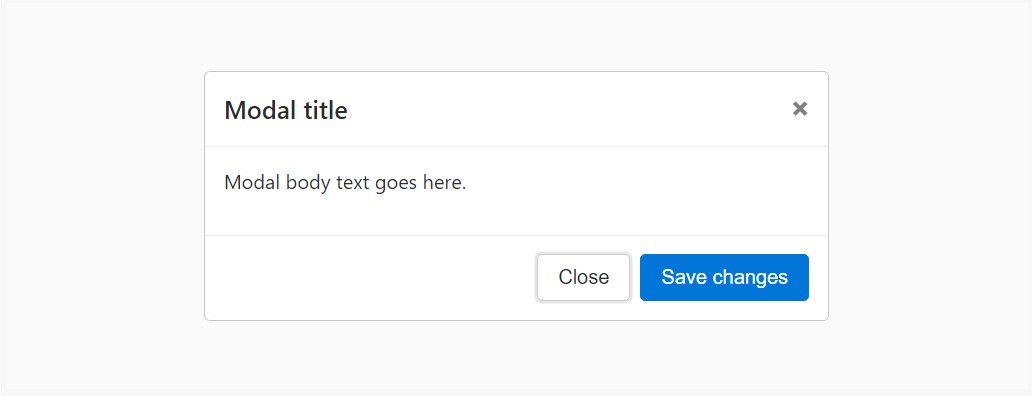
<div class="modal fade">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<p>Modal body text goes here.</p>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Live demonstration
Whenever you are going to put to use a code listed below - a working modal demo is going to be switched on as showned on the pic. It will certainly slide down and fade in from the very top of the page.
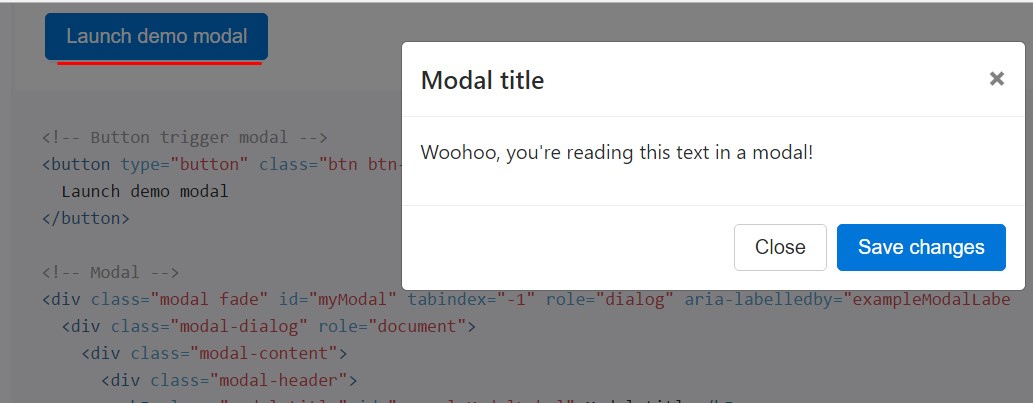
<!-- Button trigger modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal">
Launch demo modal
</button>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="myModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Scrolling expanded material
They scroll independent of the page itself when modals become too long for the user's viewport or device. Try the demo below to find what exactly we point to.
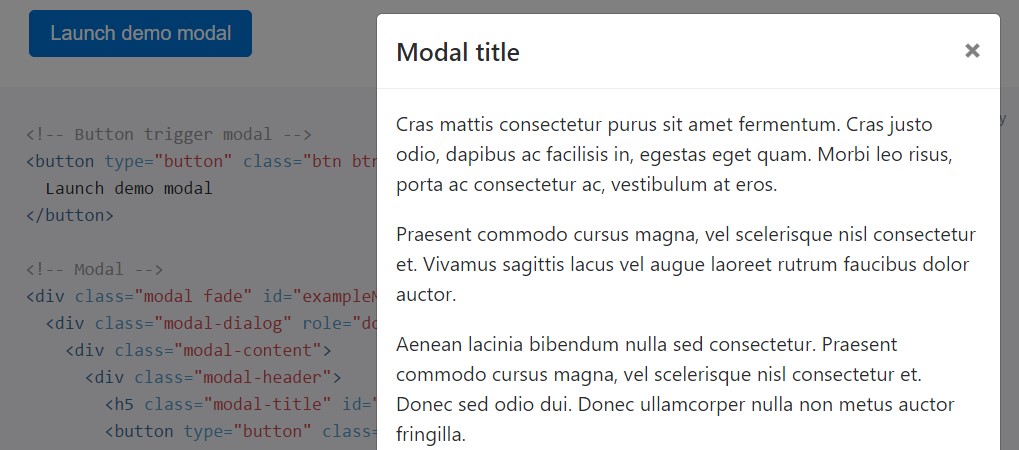
<!-- Button trigger modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModalLong">
Launch demo modal
</button>
<!-- Modal -->
<div class="modal fade" id="exampleModalLong" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLongTitle" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLongTitle">Modal title</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
...
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>Tooltips along with popovers
Tooltips along with popovers can absolutely be localised inside modals just as desired. Any tooltips and popovers within are also automatically dismissed when modals are closed.
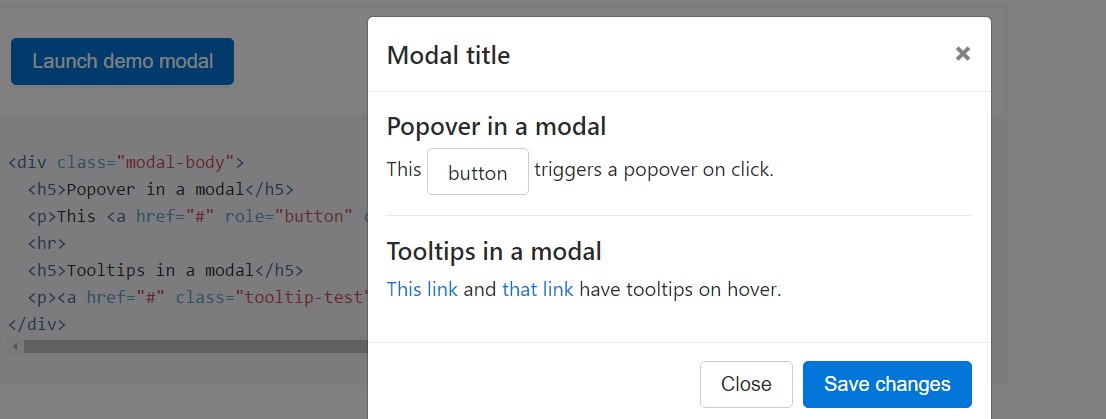
<div class="modal-body">
<h5>Popover in a modal</h5>
<p>This <a href="#" role="button" class="btn btn-secondary popover-test" title="Popover title" data-content="Popover body content is set in this attribute.">button</a> triggers a popover on click.</p>
<hr>
<h5>Tooltips in a modal</h5>
<p><a href="#" class="tooltip-test" title="Tooltip">This link</a> and <a href="#" class="tooltip-test" title="Tooltip">that link</a> have tooltips on hover.</p>
</div>Bring into play the grid
Employ the Bootstrap grid system inside a modal by simply nesting .container-fluid inside of the .modal-body. Use the normal grid system classes as you would anywhere else.
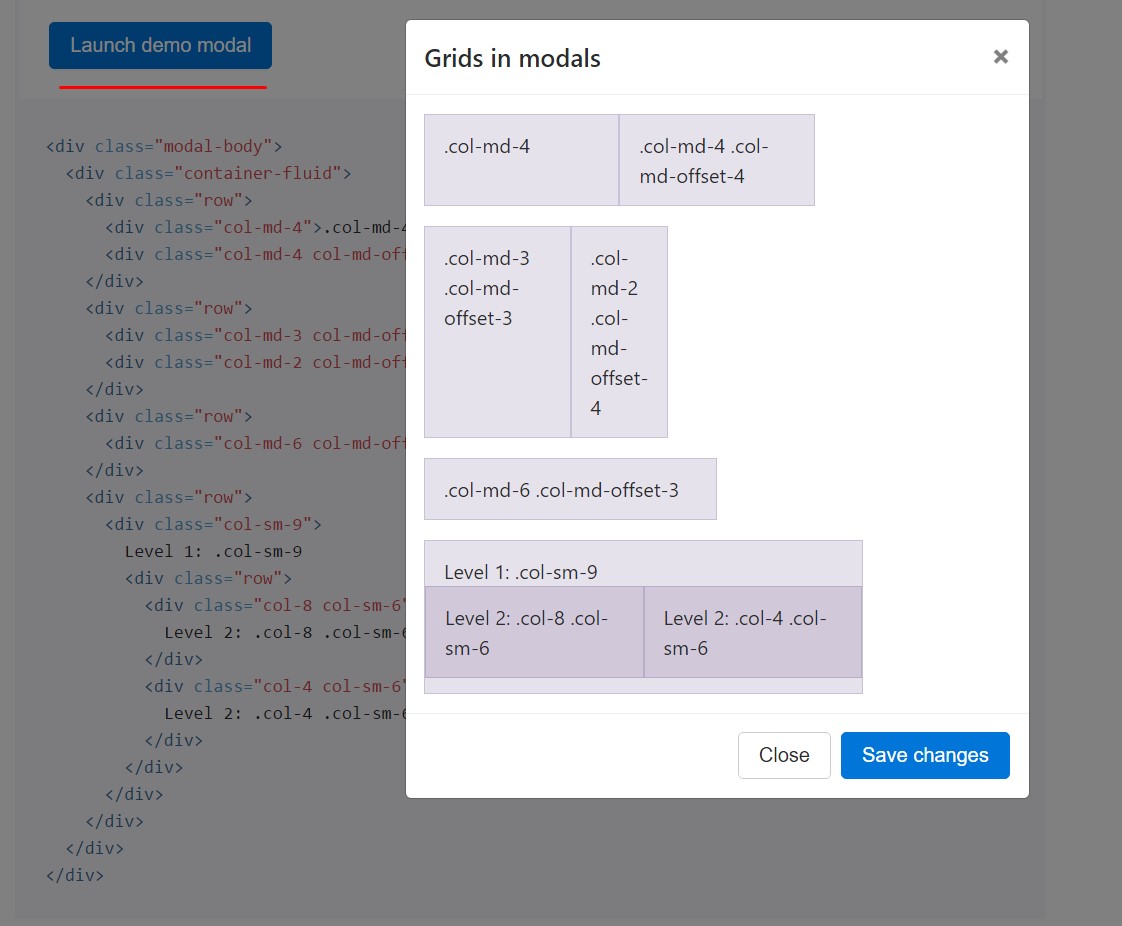
<div class="modal-body">
<div class="container-fluid">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">.col-md-4</div>
<div class="col-md-4 col-md-offset-4">.col-md-4 .col-md-offset-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-3 col-md-offset-3">.col-md-3 .col-md-offset-3</div>
<div class="col-md-2 col-md-offset-4">.col-md-2 .col-md-offset-4</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 col-md-offset-3">.col-md-6 .col-md-offset-3</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-9">
Level 1: .col-sm-9
<div class="row">
<div class="col-8 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-8 .col-sm-6
</div>
<div class="col-4 col-sm-6">
Level 2: .col-4 .col-sm-6
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>A variety of modal material
Use a group of buttons that all cause the equal modal with just a little other elements? Use event.relatedTarget and HTML data-* attributes (possibly by using jQuery) to differ the elements of the modal depending on what button was clicked.
Shown below is a live demo complied with by example HTML and JavaScript. To find out more, read the modal events files for information on
relatedTarget.
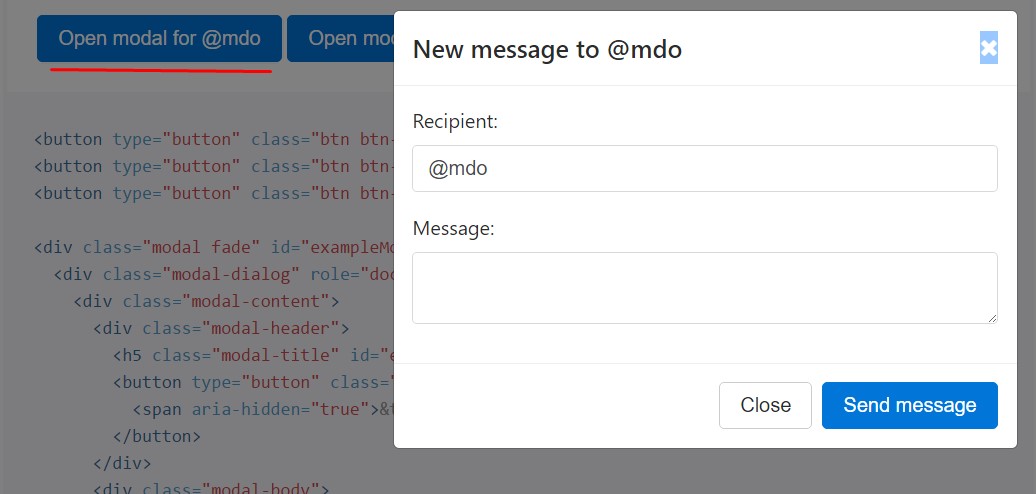
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@mdo">Open modal for @mdo</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@fat">Open modal for @fat</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#exampleModal" data-whatever="@getbootstrap">Open modal for @getbootstrap</button>
<div class="modal fade" id="exampleModal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="exampleModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<h5 class="modal-title" id="exampleModalLabel">New message</h5>
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="recipient-name" class="form-control-label">Recipient:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="recipient-name">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="message-text" class="form-control-label">Message:</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="message-text"></textarea>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Send message</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>$('#exampleModal').on('show.bs.modal', function (event)
var button = $(event.relatedTarget) // Button that triggered the modal
var recipient = button.data('whatever') // Extract info from data-* attributes
// If necessary, you could initiate an AJAX request here (and then do the updating in a callback).
// Update the modal's content. We'll use jQuery here, but you could use a data binding library or other methods instead.
var modal = $(this)
modal.find('.modal-title').text('New message to ' + recipient)
modal.find('.modal-body input').val(recipient)
)Take away animation
For modals which just simply appear instead of fade into view, eliminate the .fade class out of your modal markup.
<div class="modal" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="..." aria-hidden="true">
...
</div>Dynamic heights
Supposing that the height of a modal switch while at the same time it is open, you should summon $(' #myModal'). data(' bs.modal'). handleUpdate() to readjust the modal's position if a scrollbar appears.
Availability
Be sure to add in role="dialog" as well as aria-labelledby="...", referencing the modal title, to .modal, and role="document" to the .modal-dialog in itself. Also, you can give a information of your modal dialog using aria-describedby on .modal.
Embedding YouTube web videos
Inserting YouTube video clips in modals needs added JavaScript not in Bootstrap to instantly end playback and even more.
Optional sizes
Modals own two optionally available proportions, available through modifier classes to be put on a .modal-dialog. These sizes start at certain breakpoints to keep away from horizontal scrollbars on narrower viewports.
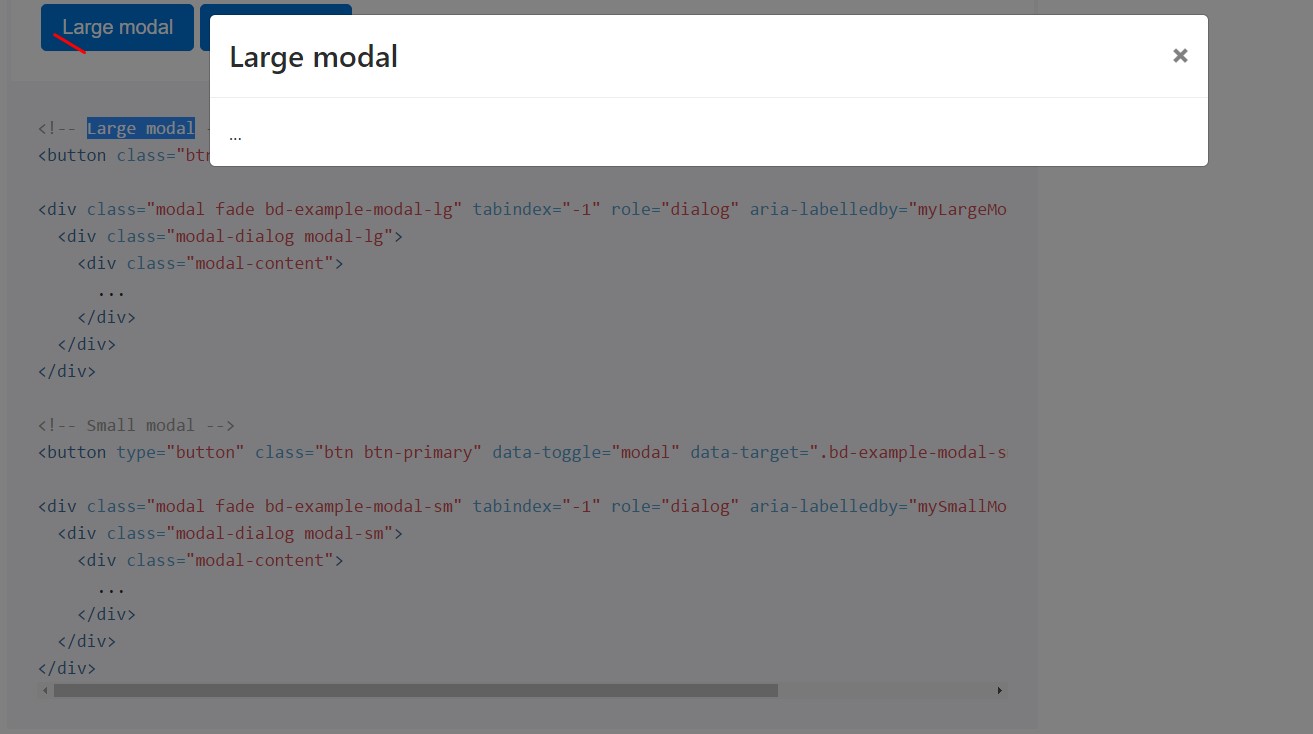
<!-- Large modal -->
<button class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target=".bd-example-modal-lg">Large modal</button>
<div class="modal fade bd-example-modal-lg" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="myLargeModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-lg">
<div class="modal-content">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>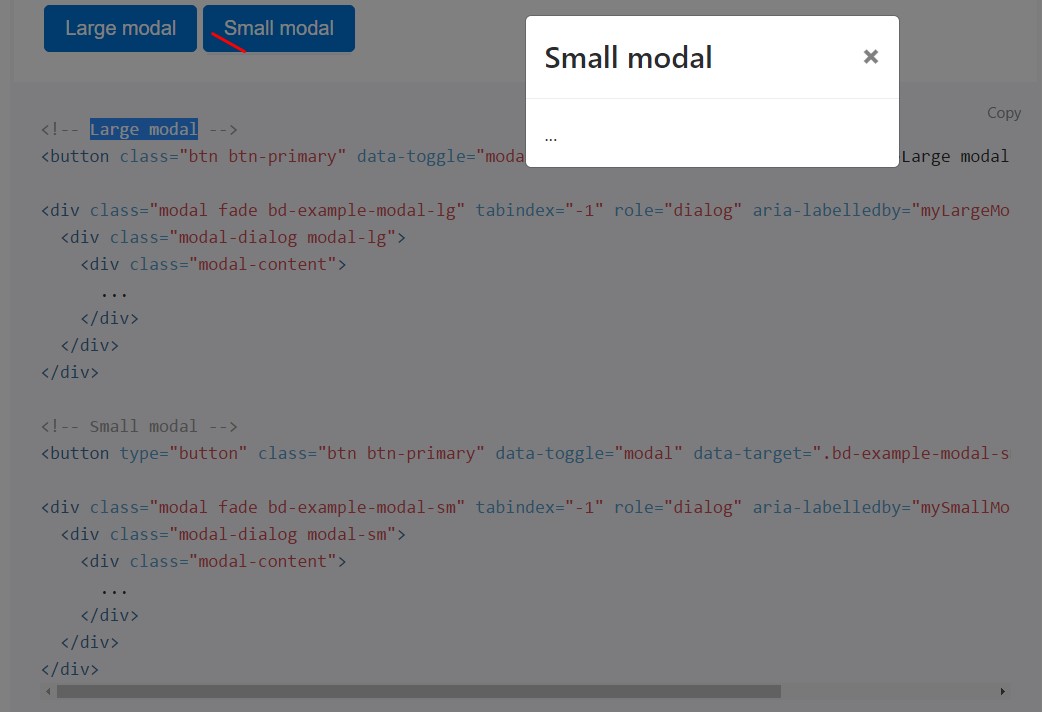
<!-- Small modal -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="modal" data-target=".bd-example-modal-sm">Small modal</button>
<div class="modal fade bd-example-modal-sm" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" aria-labelledby="mySmallModalLabel" aria-hidden="true">
<div class="modal-dialog modal-sm">
<div class="modal-content">
...
</div>
</div>
</div>Application
The modal plugin button your unseen material on demand, with information attributes or JavaScript. It even includes .modal-open to the <body> to defeat default scrolling actions and creates a .modal-backdrop to generate a mouse click zone for rejecting displayed modals at the time clicking on outside the modal.
Via data attributes
Turn on a modal without producing JavaScript. Set
data-toggle="modal" on a controller element, like a button, along with a data-target="#foo" or href="#foo" to target a certain modal to button.
<button type="button" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#myModal">Launch modal</button>Using JavaScript
Call a modal using id myModal with a one line of JavaScript:
$('#myModal'). modal( options).Opportunities
Opportunities may possibly be successfully pass via information attributes or JavaScript. For information attributes, add the option name to data-, as in data-backdrop="".
Review also the image below:
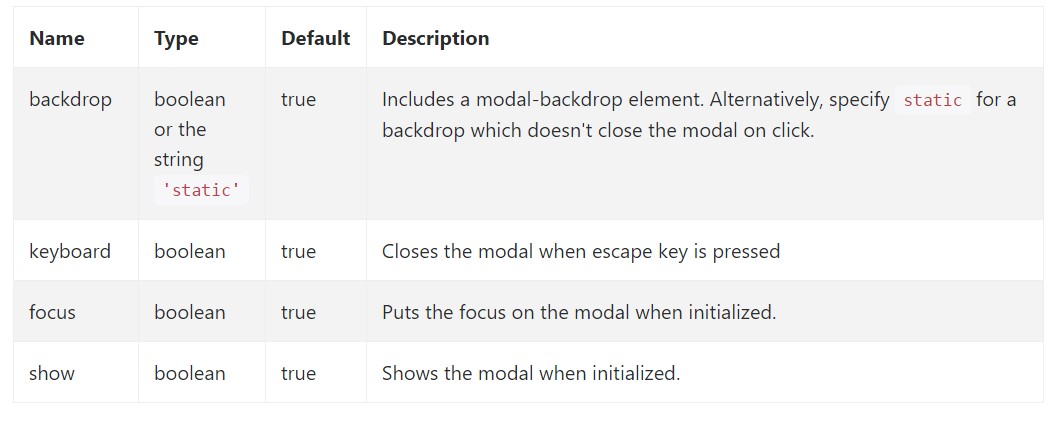
.modal(options)
Turns on your material as a modal. Takes an optionally available options object.
$('#myModal').modal(
keyboard: false
).modal('toggle')
Manually toggles a modal. Come back to the user just before the modal has really been presented or disguised (i.e. just before the shown.bs.modal or hidden.bs.modal situation happens).
$('#myModal').modal('toggle').modal('show')
Manually opens up a modal. Come back to the user before the modal has really been displayed (i.e. before the shown.bs.modal function occurs).
$('#myModal').modal('show').modal('hide')
Manually conceals a modal. Returns to the user before the modal has in fact been covered (i.e. just before the hidden.bs.modal event happens).
$('#myModal').modal('hide')Bootstrap modals events
Bootstrap's modal class exposes a few events for trapping in to modal performance. All modal events are fired at the modal itself (i.e. at the <div class="modal">).

$('#myModal').on('hidden.bs.modal', function (e)
// do something...
)Final thoughts
We experienced ways in which the modal is constructed but exactly what might probably be within it?
The answer is-- pretty much all sorts ofthings-- coming from a very long titles and forms plain part with some headings to the most complicated structure that utilizing the flexible design concepts of the Bootstrap framework might truly be a page inside the page-- it is technically achievable and the choice of applying it falls to you.
Do have in your mind however if ever at a certain point the content to be soaked the modal becomes far way too much probably the more desirable strategy would be applying the entire subject in to a separate web page in order to get practically better appearance along with utilization of the whole display screen size accessible-- modals a suggested for more compact blocks of information advising for the viewer's attention .
Review several online video short training about Bootstrap modals:
Connected topics:
Bootstrap modals: approved information

W3schools:Bootstrap modal information
Bootstrap 4 with remote modal