Bootstrap Form Elements
Intro
Bootstrap offers a handful of form manage looks, layout alternatives, along with custom components for producing a vast range of Bootstrap Form Inline.
Forms give the awesome resolution for obtaining some comments coming from the visitors of our pages. In case it is actually a basic touch or else registration form having simply just a only a few fields or a sophisticated and well thought inquiry the Bootstrap 4 platform got everything that is definitely demanded to perform the function and have great responsive appeal.
By default when it comes to the Bootstrap framework the form components are designated to span all size of its parent element-- this becomes accomplished by selecting the .form-control class and using HTML form builder. The lebels and commands need to be wrapped into a parent element with the .form-group class for optimal spacing.
Bootstrap Form Example commands
Bootstrap's form controls grow with regards to our Rebooted form designs with classes.
Put into action such classes to opt into their modified displays to get a much more regular rendering all around browsers and equipments . The sample form listed below displays typical HTML form components that acquire up-dated styles from Bootstrap together with extra classes.
Keep in mind, ever since Bootstrap employs the HTML5 doctype, all of inputs must provide a type attribute.
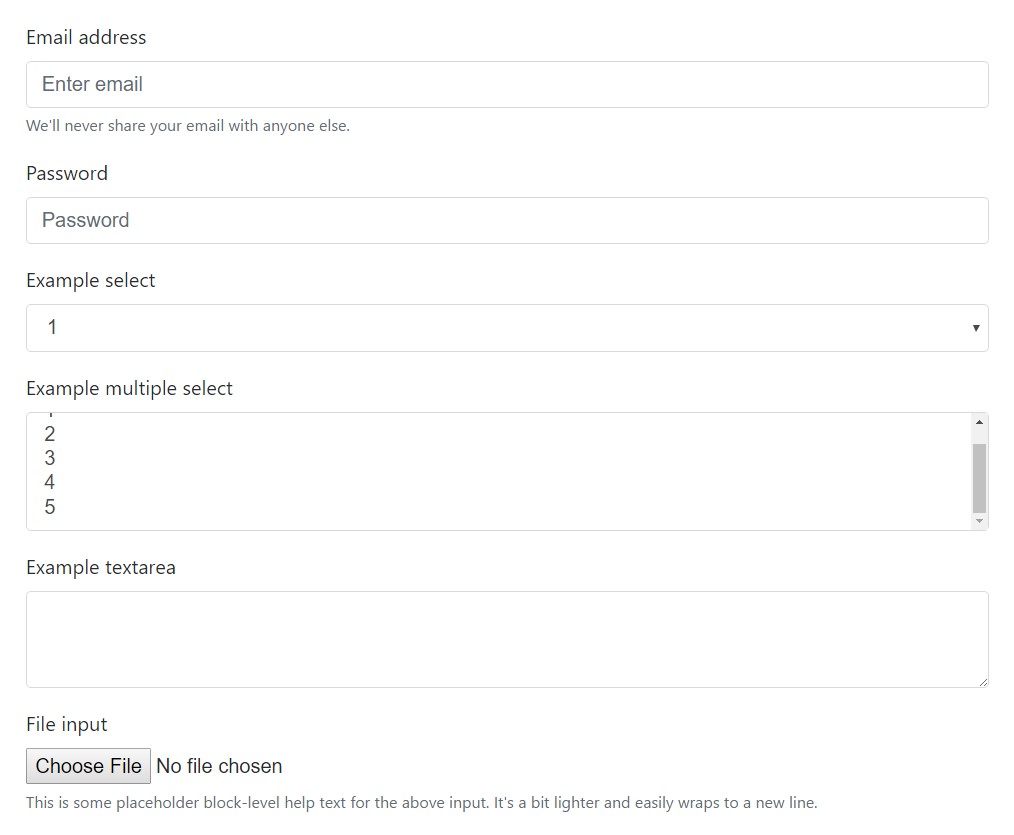
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Email address</label>
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp" placeholder="Enter email">
<small id="emailHelp" class="form-text text-muted">We'll never share your email with anyone else.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleSelect1">Example select</label>
<select class="form-control" id="exampleSelect1">
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleSelect2">Example multiple select</label>
<select multiple class="form-control" id="exampleSelect2">
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleTextarea">Example textarea</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="exampleTextarea" rows="3"></textarea>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputFile">File input</label>
<input type="file" class="form-control-file" id="exampleInputFile" aria-describedby="fileHelp">
<small id="fileHelp" class="form-text text-muted">This is some placeholder block-level help text for the above input. It's a bit lighter and easily wraps to a new line.</small>
</div>
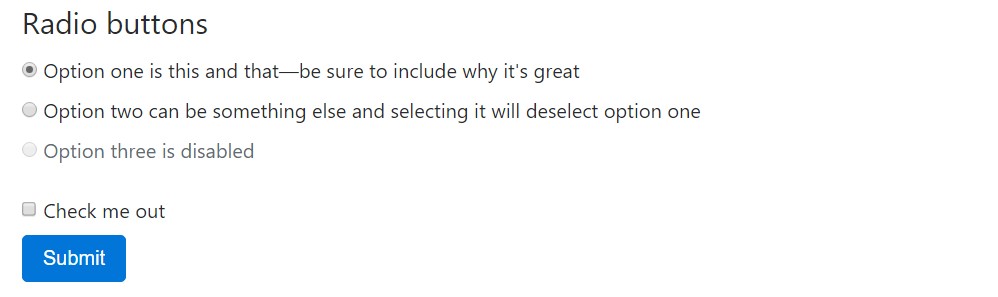
<fieldset class="form-group">
<legend>Radio buttons</legend>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>
</fieldset>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input">
Check me out
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>Below is a finished list of the specified Bootstrap Form Input regulations supported by Bootstrap as well as the classes that customise them. Supplemental documentation is offered for each and every group.
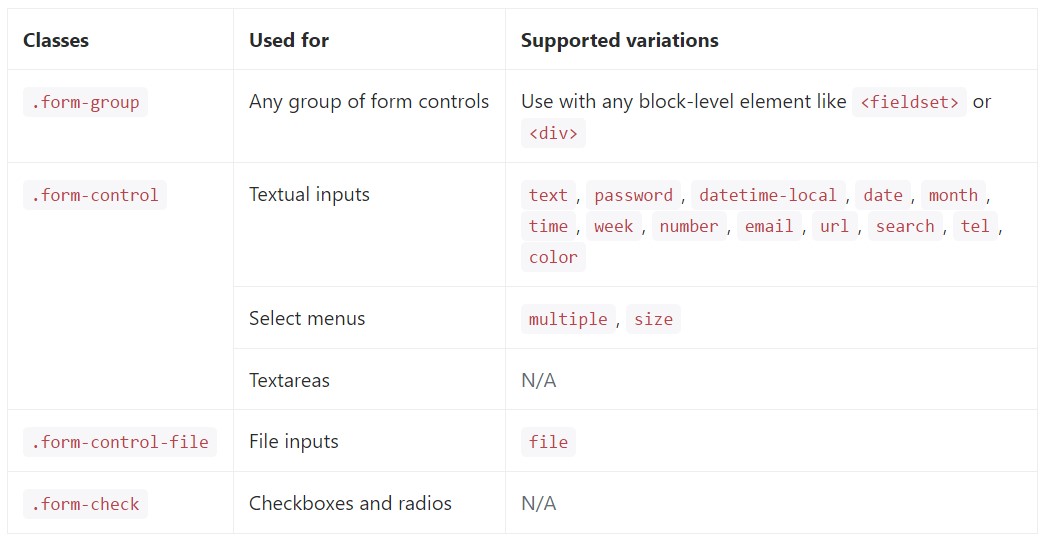
Textual inputs
Below are the samples of .form-control applied to each textual HTML5 <input> type.
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-text-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Text</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="text" value="Artisanal kale" id="example-text-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-search-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Search</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="search" value="How do I shoot web" id="example-search-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-email-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="email" value="[email protected]" id="example-email-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-url-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">URL</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="url" value="https://getbootstrap.com" id="example-url-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-tel-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Telephone</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="tel" value="1-(555)-555-5555" id="example-tel-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-password-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="password" value="hunter2" id="example-password-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-number-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Number</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="number" value="42" id="example-number-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-datetime-local-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Date and time</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="datetime-local" value="2011-08-19T13:45:00" id="example-datetime-local-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-date-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Date</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="date" value="2011-08-19" id="example-date-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-month-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Month</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="month" value="2011-08" id="example-month-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-week-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Week</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="week" value="2011-W33" id="example-week-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-time-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Time</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="time" value="13:45:00" id="example-time-input">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="example-color-input" class="col-2 col-form-label">Color</label>
<div class="col-10">
<input class="form-control" type="color" value="#563d7c" id="example-color-input">
</div>
</div>Form design and styles
Given that Bootstrap utilizes display: block and width :100% to most of our form controls, forms will probably by default stack vertically. Supplemental classes can possibly be operated to change this particular layout on a per-form basis.
Form categories
The .form-group class is the best method to provide amazing design to forms. Its primary goal is to supply margin-bottom around a label and command coupling. Just as a bonus, considering that it is actually a class you can easily make use of it utilizing <fieldset>-s, <div>-s, or else pretty much most other feature.

<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="formGroupExampleInput">Example label</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="formGroupExampleInput" placeholder="Example input">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="formGroupExampleInput2">Another label</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="formGroupExampleInput2" placeholder="Another input">
</div>
</form>Inline forms
Apply the .form-inline class to feature a variety of labels, form managements , and tabs on a particular horizontal row. Form controls inside of inline forms can be different slightly against their default conditions.
- Controls are display: flex, breaking any HTML white territory and allowing you to generate placement regulation along with spacing and flexbox utilities.
- Controls and input groups are given width: auto to override the Bootstrap default width: 100%.
- Controls exclusively appear inline in viewports which are at very least 576px big to represent small viewports on mobile devices.
You may possibly ought to personally resolve the width and alignment of individual form controls together with spacing utilities ( just as presented below) And finally, ensure to always include a <label> along with each and every form control, whether or not you require to disguise it directly from non-screenreader site visitors with a code.
<form class="form-inline">
<label class="sr-only" for="inlineFormInput">Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0" id="inlineFormInput" placeholder="Jane Doe">
<label class="sr-only" for="inlineFormInputGroup">Username</label>
<div class="input-group mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<div class="input-group-addon">@</div>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="inlineFormInputGroup" placeholder="Username">
</div>
<div class="form-check mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox"> Remember me
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>Custom form controls also selects are also assisted.
<form class="form-inline">
<label class="mr-sm-2" for="inlineFormCustomSelect">Preference</label>
<select class="custom-select mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0" id="inlineFormCustomSelect">
<option selected>Choose...</option>
<option value="1">One</option>
<option value="2">Two</option>
<option value="3">Three</option>
</select>
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox mb-2 mr-sm-2 mb-sm-0">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Remember my preference</span>
</label>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>Alternatives to covered up labels
Assistive technologies like screen readers will certainly have problem utilizing your forms in the event that you don't include a label for every single input. For all of these inline forms, you have the ability to conceal the labels using the .sr-only class. There are actually extra alternative options of supplying a label for assistive technologies, for example, the aria-label, aria-labelledby or title attribute. If none of these are present, assistive techniques may likely resort to employing the placeholder attribute, in the case that existing, however keep in mind that usage of placeholder as a substitution for some other labelling options is not actually advised.
Using the Grid
For even more structured form layouts which are in addition responsive, you can certainly implement Bootstrap's predefined grid classes as well as mixins to produce horizontal forms. Include the .row class to form groups and utilize the .col-*-* classes in order to specify the width of your controls and labels.
Be sure to add .col-form-label to your <label>-s as well so they’re vertically centered with their associated form controls. For <legend> elements, you can use .col-form-legend to make them appear similar to regular <label> elements.
<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputEmail3" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="inputEmail3" placeholder="Email">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputPassword3" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword3" placeholder="Password">
</div>
</div>
<fieldset class="form-group row">
<legend class="col-form-legend col-sm-2">Radios</legend>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="gridRadios" id="gridRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>
</div>
</fieldset>
<div class="form-group row">
<label class="col-sm-2">Checkbox</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox"> Check me out
</label>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<div class="offset-sm-2 col-sm-10">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Sign in</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Grid-based form styles at the same time support small-sized and large inputs.
<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="lgFormGroupInput" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label col-form-label-lg">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-lg" id="lgFormGroupInput" placeholder="[email protected]">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="smFormGroupInput" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label col-form-label-sm">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-sm" id="smFormGroupInput" placeholder="[email protected]">
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Checkboxes and radios
Default radios and checkboxes are enhanced upon with the aid of .form-check, a specific class for both of these input types that enhances the layout and behaviour of their HTML elements. Checkboxes are for choosing one or else a handful of selections within a list, while radios are for choosing one choice from numerous.
The disabled class will at the same time lighten the message color tone to help reveal the input's state.
Each checkbox and radio is wrapped inside a <label> for three good reasons:
- It gives a bigger hit areas for checking the control.
- It gives a semantic and helpful wrapper to help us substitute the default <input>-s.
- It produces the state of the <input> instantly, signifying no JavaScript is involved.
We hide the default <input> with opacity and employ the .custom-control-indicator to create a new unique form indicator in its place. However we just can't build a custom one because of just the <input> simply because CSS's content doesn't function on that component..
We apply the relative selector (~) for all of our <input> states-- like : checked-- to properly design our custom made form indication . While combined along with the .custom-control-description class, we can easily additionally style the text for each and every item built upon the <input>-s state.
In the checked states, we use base64 embedded SVG icons from Open Iconic. This provides us the best control for styling and positioning across browsers and devices.
Checkboxes

<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>Custom-made checkboxes are able to likewise utilize the : indeterminate pseudo class once manually determined via JavaScript (there is no obtainable HTML attribute for specifying it).

In case you're employing jQuery, something like this should really suffice:
$('.your-checkbox').prop('indeterminate', true)Radios

<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio1" name="radio" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio2" name="radio" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Or toggle this other custom radio</span>
</label>Default (stacked)
By default, any variety of checkboxes and radios which are close relative will be vertically stacked as well as effectively spaced using .form-check.
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" value="">
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" value="" disabled>
Option two is disabled
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="exampleRadios" id="exampleRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>Inline
Group checkboxes as well as radios on the identical horizontal row with providing .form-check-inline to any .form-check.

<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox1" value="option1"> 1
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox2" value="option2"> 2
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="inlineCheckbox3" value="option3" disabled> 3
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio1" value="option1"> 1
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio2" value="option2"> 2
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check form-check-inline disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="inlineRadioOptions" id="inlineRadio3" value="option3" disabled> 3
</label>
</div>Without labels
You really should not provide a content inside the <label>, the input is arranged as you would certainly need. At the moment strictly works with non-inline checkboxes and radios. Remember to also supply some type of label when it comes to assistive modern technologies ( as an example, utilizing aria-label).

<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" id="blankCheckbox" value="option1" aria-label="...">
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input class="form-check-input" type="radio" name="blankRadio" id="blankRadio1" value="option1" aria-label="...">
</label>
</div>Static managements
If you ought to insert plain text next to a form label inside a form, employ the .form-control-static class to an element of your choice.
<form>
<div class="form-group row">
<label class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<p class="form-control-static">[email protected]</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row">
<label for="inputPassword" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Password</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword" placeholder="Password">
</div>
</div>
</form>
<form class="form-inline">
<div class="form-group">
<label class="sr-only">Email</label>
<p class="form-control-static">[email protected]</p>
</div>
<div class="form-group mx-sm-3">
<label for="inputPassword2" class="sr-only">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="inputPassword2" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Confirm identity</button>
</form>Disabled status
Add in the disabled boolean attribute for an input to avoid user interactions. Disabled inputs show up lighter plus include a not-allowed cursor.
<input class="form-control" id="disabledInput" type="text" placeholder="Disabled input here..." disabled>Add in the disabled attribute to a <fieldset> to disable all of the commands inside.

<form>
<fieldset disabled>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="disabledTextInput">Disabled input</label>
<input type="text" id="disabledTextInput" class="form-control" placeholder="Disabled input">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="disabledSelect">Disabled select menu</label>
<select id="disabledSelect" class="form-control">
<option>Disabled select</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="checkbox">
<label>
<input type="checkbox"> Can't check this
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</fieldset>
</form>Caveat regarding to web link functions of <a>
By default, web browsers are going to handle all of the essential form controls (<input>, <select> plus <button> features) inside a <fieldset disabled> as disabled, evading both the computer keyboard plus computer mouse interplays on them. However, in the case that your form additionally provides <a ... class="btn btn-*"> elements, these are going to just be offered a format of pointer-events: none. Just as indicated within the section on disabled state for buttons (and esspecially in the sub-section for anchor elements ), this CSS feature is not really yet standardized and also isn't actually entirely promoted in Opera 18 and below, as well as in Internet Explorer 11, and will not evade key board users from having the ability to focus or trigger these urls. And so to get protected, use custom-made JavaScript to disable this kind of hyperlinks.
Cross-browser consonance
Though Bootstrap will employ all of these designs within all of the web browsers, Internet Explorer 11 and below don't totally sustain the disabled attribute on a <fieldset>.Use custom JavaScript to disable the fieldset in all of these browsers.
Readonly inputs
Provide the readonly boolean attribute on an input to prevent modification of the input's value. Read-only inputs appear lighter ( similar to disabled inputs), but hold the regular cursor.

<input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Readonly input here…" readonly>Control proportions
Set heights working with classes like .form-control-lg, and set on widths working with grid column classes such as .col-lg-*.
<input class="form-control form-control-lg" type="text" placeholder=".form-control-lg">
<input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Default input">
<input class="form-control form-control-sm" type="text" placeholder=".form-control-sm">
<select class="form-control form-control-lg">
<option>Large select</option>
</select>
<select class="form-control">
<option>Default select</option>
</select>
<select class="form-control form-control-sm">
<option>Small select</option>
</select>Column sizes
Wrap inputs in a grid columns, as well as any kind of customized parent component, in order to efficiently implement the needed widths.
<div class="row">
<div class="col-2">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-2">
</div>
<div class="col-3">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-3">
</div>
<div class="col-4">
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder=".col-4">
</div>
</div>Assist text
The .help-block class is certainly cast off within the new version. If you need to put special extra message in order to help your website visitors to better get around - utilize the .form-text class preferably. Bootstrap 4 has fascinating set up in validation designs for the form controls being applied . Within this version the .has-feedback class has been simply declined-- it is really no longer really needed along with the introduction of the .form-control-danger, .form-control-warning and .form-control-success classes adding in a compact data icon straight in the input fields.
Affiliating support message with form controls
Help content ought to be explicitly connected with the form control it really relates to working with the aria-describedby attribute. This will definitely ensure that the assistive technologies-- like screen readers-- will declare this support text message the moment the user focuses or gets in the control.
Block level
Block support content-- for below inputs as well as for much longer lines of the help text message-- can be quickly obtained utilizing .form-text. This specific class includes display: block and brings in some top margin for simple spacing from the inputs mentioned earlier.
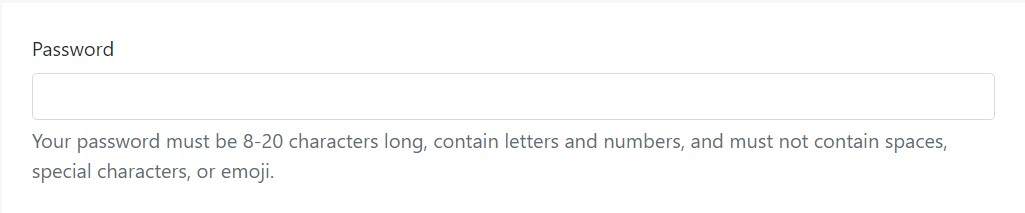
<label for="inputPassword5">Password</label>
<input type="password" id="inputPassword5" class="form-control" aria-describedby="passwordHelpBlock">
<p id="passwordHelpBlock" class="form-text text-muted">
Your password must be 8-20 characters long, contain letters and numbers, and must not contain spaces, special characters, or emoji.
</p>Inline
Inline message are able to employ any type of standard inline HTML element (be it a , <span>, or else something else).
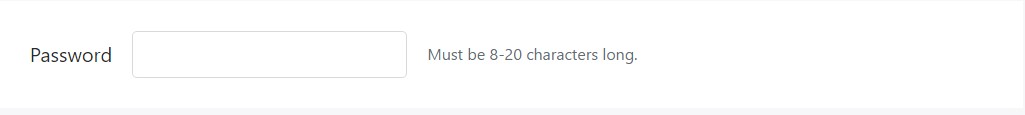
<form class="form-inline">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="inputPassword4">Password</label>
<input type="password" id="inputPassword4" class="form-control mx-sm-3" aria-describedby="passwordHelpInline">
<small id="passwordHelpInline" class="text-muted">
Must be 8-20 characters long.
</small>
</div>
</form>Validation
Bootstrap provides validation designs for danger, warning, and success states on a large number of form controls.
How to put to use
Here's a review of precisely how they work:
- To make use of, bring in .has-warning, .has-danger, or .has-success to the parent element. Any sort of .col-form-label, .form-control, or custom form component will receive the validation designs.
- Contextual validation text, besides your typical form area assistance text message, may possibly be added in with the application of .form-control-feedback. This text is going to adapt to the parent .has-* class. By default it just utilizes a little bit of margin for spacing and also a transformed color for each state.
- Validation icons are url()-s configured by using Sass variables which are applied to background-image declarations for every state.
- You can make use of your special base64 PNGs or maybe SVGs simply by updating the Sass variables and recompiling.
- Icons have the ability to additionally be disabled totally simply by preparing the variables to none as well as commenting out the source Sass.
Determining states
Usually stating, you'll want to employ a particular state for specified sorts of responses:
- Danger is ideal for the moment there's a blocking or else needed field. A user must complete this particular field appropriately to provide the form.
- Warning performs effectively for input values that are in development, such as parole strength, or soft validation right before a user attempts to submit a form.
- And as a final point, success is suitable for conditions as you have per-field validation all throughout a form and also wish to urge a user through the other fields.
Situations
Here are some cases of the aforementioned classes in action. First up is your usual left-aligned fields together with labels, support text, and validation messaging.

<div class="form-group has-success">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputSuccess1">Input with success</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-success" id="inputSuccess1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Success! You've done it.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-warning">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputWarning1">Input with warning</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-warning" id="inputWarning1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Shucks, check the formatting of that and try again.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-danger">
<label class="form-control-label" for="inputDanger1">Input with danger</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control form-control-danger" id="inputDanger1">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Sorry, that username's taken. Try another?</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>All those same states can easily also be employed together with horizontal forms.

<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="form-group row has-success">
<label for="inputHorizontalSuccess" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-success" id="inputHorizontalSuccess" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Success! You've done it.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row has-warning">
<label for="inputHorizontalWarning" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-warning" id="inputHorizontalWarning" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Shucks, check the formatting of that and try again.</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group row has-danger">
<label for="inputHorizontalDnger" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control form-control-danger" id="inputHorizontalDnger" placeholder="[email protected]">
<div class="form-control-feedback">Sorry, that username's taken. Try another?</div>
<small class="form-text text-muted">Example help text that remains unchanged.</small>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>Radios and checkboxes happen to be also maintained.

<div class="form-check has-success">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxSuccess" value="option1">
Checkbox with success
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check has-warning">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxWarning" value="option1">
Checkbox with warning
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check has-danger">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input" id="checkboxDanger" value="option1">
Checkbox with danger
</label>
</div>Customized forms
To get even more modification as well as cross web browser likeness, work with Bootstrap fully custom form features to remove and replace the web browser defaults. They're built on very top of semantic and available markup, in this way they are really stable alternatives for any type of default form control.
Disabled
Custom checkboxes and radios can additionally be disabled . Add the disabled boolean attribute to the <input> plus the custom made indicator and label explanation will be automatically designated.
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input" disabled>
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radio3" name="radioDisabled" type="radio" class="custom-control-input" disabled>
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>Validation conditions
Add the other states to your custom made forms having Bootstrap validation classes.

<div class="form-group has-success">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-warning">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-group has-danger mb-0">
<label class="custom-control custom-checkbox">
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Check this custom checkbox</span>
</label>
</div>Stacked
Custom-made radios and checkboxes are inline to start. Provide a parent along with class .custom-controls-stacked to make certain each form control is on different lines.

<div class="custom-controls-stacked">
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radioStacked1" name="radio-stacked" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Toggle this custom radio</span>
</label>
<label class="custom-control custom-radio">
<input id="radioStacked2" name="radio-stacked" type="radio" class="custom-control-input">
<span class="custom-control-indicator"></span>
<span class="custom-control-description">Or toggle this other custom radio</span>
</label>
</div>Select menu
Custom made <select> menus require simply just a customized class, .custom-select to activate the customized styles.
<select class="custom-select">
<option selected>Open this select menu</option>
<option value="1">One</option>
<option value="2">Two</option>
<option value="3">Three</option>
</select>File web browser
The file input is the very most keen of the group and need additional JavaScript in the case that you would love to hook them up along with practical Choose file ... and selected file name text message.
<label class="custom-file">
<input type="file" id="file" class="custom-file-input">
<span class="custom-file-control"></span>
</label>Here’s the best ways to operate:
- We wrap the <input> inside a <label> so the custom made control efficiently sets off the file browser.
- We cover up the default file <input> via opacity.
- We apply : after in order to produce a custom-made background and directive (Choose file ...).
- We utilize :before to develop and position the Internet browser button.
- We announce a height on the <input> for suitable spacing for surrounding web content .
Simply puts, it is really an absolutely custom-made element, all developed using CSS.
Interpreting alternatively customing the sequences
The : lang() pseudo-class is utilized to enable simple adaptation of the "Browse" as well as "Choose file ..." text in to other languages. Just simply override or incorporate access to the $ custom-file-text SCSS variable along with the associated language mark and localized strings. The English strings can possibly be customized the same way. For example, here's precisely how one could possibly include a Spanish adaptation (Spanish's language code is es)
$custom-file-text: (
placeholder: (
en: "Choose file...",
es: "Seleccionar archivo..."
),
button-label: (
en: "Browse",
es: "Navegar"
)
);You'll ought to determine the language of your file (or subtree thereof) appropriately in order for the suitable text message to be presented. This may be accomplished working with the lang attribute as well as the Content-Language HTTP header, amongst other options.
Final thoughts
Generally all of these are the brand-new elements to the form components introduced within the most recent fourth version of the Bootstrap framework. The overall perception is the classes got more instinctive and explicit because of this-- much more convenient to use and also utilizing the custom-made control elements we can easily now get a lot more expected visual aspect of the elements we involve in the web pages we create. And now everything that is actually left for us is figure out the appropriate information we would need from our possible site visitors to submit.
Ways to work with the Bootstrap forms:
Linked topics:
Bootstrap forms main documents
Bootstrap tutorial
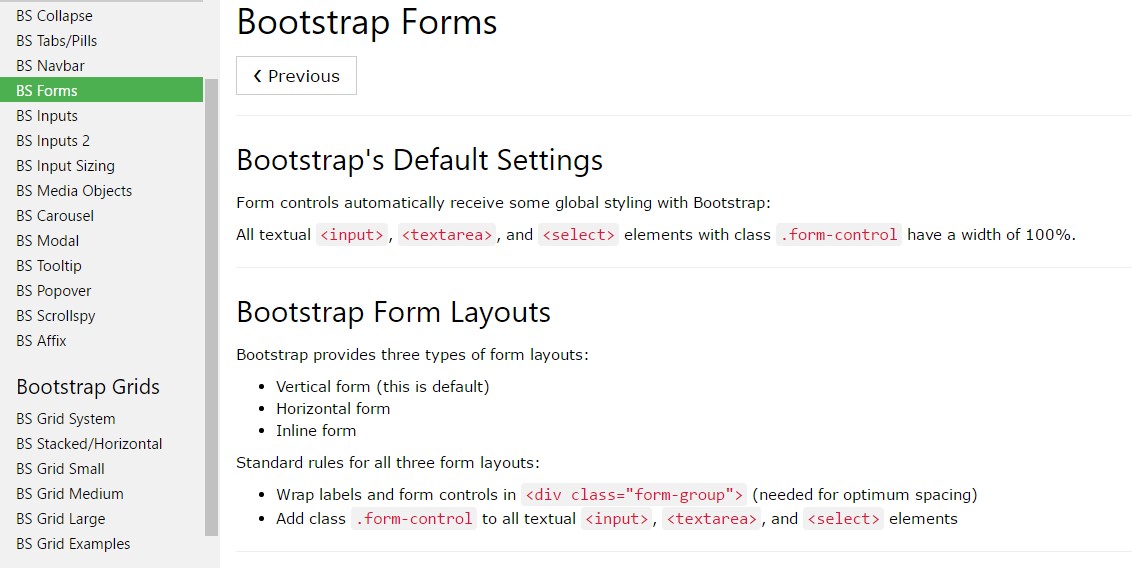
Support for Bootstrap Forms
Why do not we examine AMP project and AMP-form component?